CBSE Class 10 Science (086) Sample Question Paper 2025-26 with Marking Scheme / Solution – PDF Download
CBSE has released the Class 10 Science (Code 086) Sample Question Paper 2026 with Solution, based on the revised assessment pattern applicable from the academic session 2025–26. The question paper design has been updated to make evaluation more comprehensive and subject-specific.
As per the latest format, the paper is now divided into three distinct sections: Section A – Biology (30 Marks), Section B – Chemistry (25 Marks) and Section C – Physics (25 Marks)
- Each section focuses on subject-specific understanding, making preparation more organized.
- Questions include a mix of objective, short answer, long answer, and competency-based formats, aligned with the revised learning outcomes.
- This structure helps students strengthen concept clarity and application-based skills, which are vital for scoring high in Science.
This sample paper is an essential resource for students aiming to excel in the upcoming board exams. Download the Previous Year Question Papers with detailed solutions and start practicing today to improve your performance and accuracy.

SCIENCE (Code 086) – SQP with Solution
(Session 2025-26)
Time allowed : 3 hours
Maximum Marks : 80
General Instructions :
(i) This question paper consists of 39 questions in 3 sections. Section A is Biology, Section B is Chemistry and Section C is Physics.
(ii) All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
SECTION – A (BIOLOGY – 30 Marks)
Question 1 to 16 are multiple choice questions. Only one of the choices is correct. Select and write the correct choice as well as the answer to these questions.
1. Select the group in which all organisms have the same mode of nutrition. (1)
A. Cuscuta, yeast, legumes, leeches and tapeworm
B. Cactus, ticks, lice, leeches and cow
C. Cuscuta, ticks, lice, leeches and tapeworm
D. Cactus, grass, lice, lion and tapeworm
2. of the glucose in our muscle cells when there is lack of oxygen? (1)
A. Ethanol + carbon dioxide + Energy
B. Lactic acid + Energy
C. Lactic acid + carbon monoxide + Energy
D. Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
3. Which of the following is a correct combination of function and part of the brain? (1)
A. Posture and balance: Cerebrum
B. Salivation: Medulla in midbrain
C. Hunger: Pons in hindbrain
D. Blood pressure: Medulla in hindbrain
4. The blood glucose level in a patient was very high. It may be due to inadequate secretion of: (1)
A. growth hormone from pituitary gland
B. oestrogen from ovary
C. insulin from pituitary gland
D. insulin from pancreas
5. In a cross between black furred rabbit (B) and white furred rabbit (b), all offspring were found to have black fur. What can be inferred about the genetic makeup of the parent rabbits (1)
A. BB X bb
B. Bb X Bb
C. Bb X bb
D. bb X bb
6. Which are the correct statements related to ozone? (1)
(i) Ozone layer helps in increasing the UV radiations reaching earth.
(ii) Ozone is a deadly poison.
(iii) Ozone layer shields the earth from UV radiations.
(iv) Ozone layer prevents UV rays which cause skin cancer.
(v) Ozone is formed with the help of Chloroflurocarbons.
Options:
A. (i), (ii), (iii)
B. (ii), (iii), (iv)
C. (iii), (iv), (v)
D. (i), (iv), (v)
7. Which of the following human activities has resulted in an increase of non-biodegradable substances? (1)
A. Organic farming
B. Increase in tree plantation
C. Use of plastic as packaging material
D. Composting of kitchen waste
8. Assertion (A): Tallness of a pea plant is controlled by an enzyme.
Reason (R): The gene for that enzyme makes proteins which help the plant to be tall. (1)
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A
C. A is true but R is false
D. A is false but R is true
9. Assertion (A): Vulture will always have the least amount of pesticides in a food chain.
Reason (R): Vulture occupies the last trophic level and it gets only 10% of energy of the previous trophic level. (1)
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A
C. A is true but R is false
D. A is false but R is true
10. Unlike animals, plants do not have any excretory products as they do not eat food. Comment upon the statement with justification. (2)
Ans: It is completely wrong to say that plants do not produce any excretory products.
However, plants use completely different strategies for excretion than those of the animals. They get rid of these wastes in different manner:
i. Oxygen, a photosynthetic waste, is removed through stomata.
ii. Excess water is removed by transpiration through stomata.
11. Students to attempt either option A or B.
A. How many chambers are there in the heart of the following organisms? How is mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood prevented in their body? (2)
(i) Fishes
Ans: There are two chambers in the heart of fish. The blood is pumped to the gills, is oxygenated there and passes directly to the rest of the body.
(ii) Humans
Ans: There are four chambers in the heart of a human being. Separation of the right side and the left side of the heart by septum prevents mixing of oxygenated and de-oxygenated bloods.
OR
B. Explain the mechanism by which the water is transported in plants?
Ans: Xylem moves water and minerals obtained from the soil through roots to all other parts of the plant in a unidirectional manner// Transpiration takes place from leaf which causes a transpirational pull in the tracheids and vessels of xylem facilitating upward movement of water// roots actively uptake ions from the soil, leading to difference in concentration gradient, thereby water moves into the roots to eliminate this difference/ creating a steady movement of water into root xylem.
12. About 100 acres of forest land was declared as Natural reserve park. The following organisms were predominant in the Natural reserve park: (2)
rabbit, frog, grass, fish, fox, water insects, zebra, peacock, snake, trees, bird, owl, insects, tiger, vulture, duck. Create a food web comprising two separate food chains with different producers by using the above data.
Ans: Tree food chain: tree, zebra, tiger
Grassland food chain: grass, zebra, tiger
Food web: Join the two food chains at a common point (zebra)
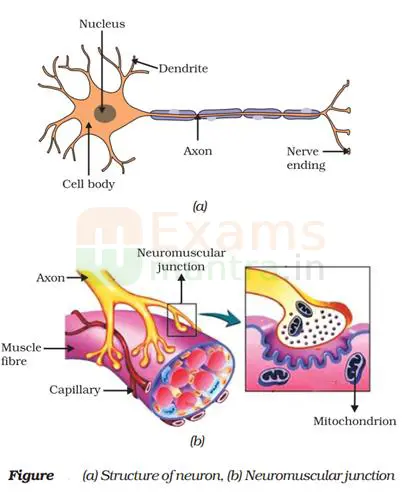
13. Draw and explain how the nerve cells help in transmission of impulses? (3)
Ans: All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells. The information acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell (Fig. a), sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse.
This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals.
These chemicals cross the gap, or synapse, and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron. This is how nervous impulses travel in the body. (Fig b).
14. In a genetic experiment, plants with pure round green seeds (RRyy) were crossed with plants with wrinkled yellow seeds (rrYY). (3)
(i) Show the gametes formed when F1 was self-pollinated.
Ans: RY, Ry, rY, ry
(ii) A total of 144 seeds were produced which developed into saplings. Show the ratio in which these traits are independently inherited in these144 sapling.
Ans: The traits which are independently inherited are as follows
Tall round: 81
Tall wrinkled: 27
Short round: 27
Short wrinkled: 9
(Ratio :- 9 : 3 : 3 : 1)
15. Neha consumed boiled sweet potatoes and boiled eggs for breakfast. Help her to understand some steps in the process of digestion of the food taken by her by answering the questions given below. (4)
Attempt either subpart A or B.
A. Which of these food items is rich in proteins? In which part of the alimentary canal is the digestion of this component initiated? Name the enzymes, conditions required and the glands associated with the digestion here.
Ans: Eggs are rich in proteins. The digestion of proteins is initiated in the stomach. Gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach release hydrochloric acid, a protein digesting enzyme called pepsin and mucus. The hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin.
OR
B. Which of these food items contains fats? How is it digested?
Ans: Eggs contain fats. Bile juice from the liver breaks down large fat globules into smaller ones for increasing the efficiency of the enzymes and making the medium alkaline. Emulsified fats are digested by lipase secreted by pancreas.
C. Which of these food items is rich in starch? How is its digestion initiated?
Ans: Sweet potatoes are rich in starch. The saliva secreted by salivary glands present in buccal cavity contain an enzyme called salivary amylase that breaks down starch which is a complex molecule to give sugar.
D. The figure given below represents parts of the human alimentary canal. Which of these parts will have the maximum amount of digested food as soon as the process of digestion is completed?
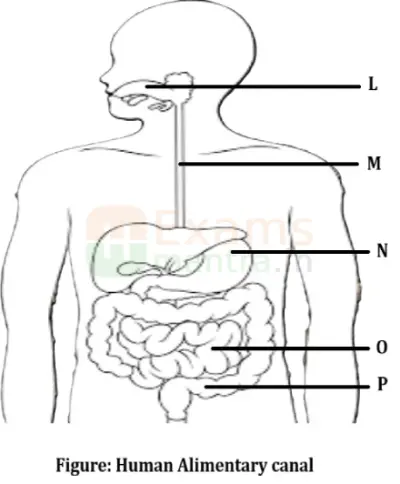
Ans: Small Intestine will have a maximum amount of digested food as the process of digestion is completed in the small intestine.
16. Attempt either option A or B.
A. Puneet wanted to grow banana plants. (5)
(i) Based on your knowledge on plant reproduction should he opt for seeds or any alternate method of reproduction. Justify your answer.
Ans: Puneet should not choose seeds as banana plants have lost the capacity to produce seeds. He should go for vegetative propagation of banana (by stem cutting).
(ii) Offsprings of a banana plant usually show very little variation. What causes variation and are variations good or bad? Justify.
Ans: Errors and variations in DNA copying cause variation. Variation is good as it can help a population tide over unfavourable conditions by survival of some variants. It is bad as parents’ desirable characters are lost/ sometimes variants are not able to survive in the new conditions/ the variant is not able to use the cellular apparatus efficiently.
OR
B. Annie was conducting research on the number of fruits produced by watermelon under different conditions. She grew 25 watermelon plants each in both glass house A and B. She introduced pollinators in glass house A only.
(i) What difference will she observe in the number of fruits produced in the two glass houses? Explain with reason.
Ans: Watermelon has unisexual flowers, the male and female flowers are separate. The presence of pollinators will facilitate cross pollination between the flowers increasing the chance of fertilization and number of fruits being produced. Without pollinators the probability of pollen falling on stigma reduces in a unisexual flower, especially if they are far apart thus the number of fruits produced will be less.
(ii) List 3 changes that will occur in a flower once it gets fertilized.
Ans: The three changes observed are:
● Ovule develops a tough coat and becomes seed.
● Ovary grows and ripens to form fruit.
● Petals, sepals, stamen, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
SECTION – B (CHEMISTRY – 25 Marks)
17. Which of the following equations represent redox reactions and what are the values for ‘p’ and ‘q’ in these equations? (1)
Equation 1: Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → Al2O3 (s) + p Fe(l) + heat
Equation 2: 2C4H10(g) + 13O2(g) →△→ 8CO2(g)+ q H2O(g)
A. Only equation 1 is a redox reaction, p =1 and q=3
B. Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p= 2 and q=4
C. Only equation 2 is a redox reaction, p= 2 and q= 10
D. Both equations 1 and 2 are redox reactions, p= 2 and q=10
18. Four statements about the reactions of oxides with dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide are listed. (1)
I. Aluminium oxide reacts with both dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
II. Calcium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
III. Zinc oxide reacts with both dilute hydrochloric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
IV. Sulphur dioxide does not react with either dilute hydrochloric acid or aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Which statements are correct?
A. I and II
B. I and III
C. II and IV
D. III and IV
19. An iron nail is added to each of the two test tubes ‘P’ and ‘Q’ containing aqueous copper (II) sulphate, and aqueous silver nitrate respectively. Which of the following observation is correct? (1)
A. In test tube ‘P’ iron nail is coated with a blue coating and in test tube ‘Q’ there is no reaction
B. Iron nail is coated with a brown coating in test tube ‘P’ and silver coating in test tube ‘Q’
C. There is no reaction in either of the test tubes ‘P’ or ‘Q’
D. There is no reaction in test tube ‘P’ but a silver coating on iron nail is seen in test tube ‘Q’
20. Methyl orange is added to dilute hydrochloric acid and to aqueous sodium hydroxide. What is the colour of the methyl orange in each solution? (1)
| Sample | colour in dilute hydrochloric acid | colour in aqueous sodium hydroxide |
|---|---|---|
| A | Orange | Red |
| B | Red | Yellow |
| C | Red | Orange |
| D | Yellow | Red |
21. Which of the following substances when dissolved in equal volume of water, will have the highest pH value? (1)
A. Sulphuric acid
B. Acetic acid
C. Magnesium hydroxide
D. Sodium hydroxide
22. When excess of carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, the milkiness disappears because (1)
A. water soluble calcium carbonate converts to water soluble calcium bicarbonate
B. insoluble calcium carbonate converts to water soluble calcium bicarbonate
C. water soluble calcium carbonate converts to insoluble calcium bicarbonate
D. insoluble calcium carbonate converts to insoluble calcium bicarbonate
23. In the reaction of aqueous solution of barium chloride with aqueous solution of sodium sulphate, the aqueous solution formed will be: (1)
A. BaCl2
B. BaSO4
C. Na2SO4
D. NaCl
24. Assertion (A): C4H8, C4H6 and C4H10 are members of the same homologous series
Reason (R): C4H8, C4H6, C3H4, C3H6, C2H4, C2H2 are unsaturated hydrocarbons. (1)
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A
C. A is true but R is false
D. A is false but R is true
25. The following activity is set-up in the science lab by the teacher.
He clamped an aluminium wire on a stand and fixed a pin to the free end of the wire using wax. Then he heated the wire with a burner from the end where the wire is clamped. Students observed the pin fall off. (2)
A. If the teacher replaces aluminium wire by silver wire, will the students’ observation change? Justify your answer.
Ans: The pin will drop but will take less time to drop because silver is a better conductor of heat than aluminium.
B. Will the aluminium wire melt? Give reason for your answer.
Ans: No, aluminium wire will not melt because metals have high melting points.
26. Attempt either option A or B.
A. An element ‘X’ is stored in kerosene, and cannot be extracted from its ore using a reducing agent. ‘X’ forms an ionic compound on reaction with chlorine. (3)
(i) Can we store ‘X’ in water? Give reason to support your answer.
Ans: No, ‘X’ is highly reactive and will catch fire.
(ii) Identify element ‘X’. Name the process used and write the equation for extraction of ‘X’ from its ore.
Ans: It is extracted from molten sodium chloride by electrolytic reduction
Cathode: Na+ + e– → Na
Anode: 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
(Potassium is also a correct option)
OR
B. The domes of many building in Europe are made of copper. These domes now appear greenish in colour.
(i) Why do the domes appear greenish though copper is orange-red in colour?
Ans: Copper gets oxidised/corroded to basic copper carbonate which is greenish in colour.
(ii) In your opinion, should the copper domes be replaced by iron domes to overcome the problem of change of colour of copper domes?
Ans: No, iron will rust and the reddish layer of rust will come off exposing iron to air, the dome will not be stable. Copper on the other hand on corrosion forms a protective layer which does not allow further corrosion.
(iii) Domes used to be made from thin sheets of metals. Why did the ancient architects use copper to make domes?
Ans: Copper is a highly malleable metal, its thin sheets can be used to give different shapes of roofs, like the shape of a dome.
27. Amrita electrolysed distilled water using the set-up shown in figure 1. She was expecting two gases to be evolved at the anode and cathode respectively (3) fig 1
fig 1
Suddenly, she realised that the bulb in the circuit did not glow when she used distilled water (figure 2) fig 2
fig 2
After this realization, she added a substance to the distilled water for electrolysis to take place.
Answer the following questions based on the information given above:
A. Which gas was she expecting to be formed at the anode and which one at the cathode respectively?
Ans: She was expecting Oxygen gas to be formed at the anode and hydrogen at the cathode.
B. Why did the bulb not glow when Amrita passed electricity through distilled water?
Ans: Distilled water is a poor conductor of electricity.
C. Which substance was added by Amrita to distilled water to get the expected result?
Ans: Adding few drops of H2SO4 or some NaCl (or any other strong electrolyte)
28. Sara took 2 mL of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube and added two drops of phenolphthalein solution to it. The solution turned pink in colour. She added dilute H2SO4 to the above solution drop by drop until the solution in the test tube became colourless. 40 drops of dilute H2SO4 were used for the change in colour from pink to colourless. When Sara added a drop of NaOH to the solution, the colour changed to back to pink again. (4)
Sara now tried the activity with different volumes of NaOH and recorded her observation in the table given below:
| S. No. | Volume of dil. NaOH taken (mL) | Drops of dil. H2SO4 used |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 20 |
| 2 | 3 | 30 |
| 3 | 4 | 40 |
Answer the following questions based on the above information:
A. If Sara used concentrated H2SO4 in place of dilute H2SO4, how many drops will be required for the change in colour to be observed?
(a) 40 (b) < 40 (c) >40
Justify your answer.
Ans: (b) < 40, because concentrated H2SO4 gives more H+ ions than dilute acid.
B. Sara measured 20 drops of dil. H2SO4 and found its volume to be 1 mL. If Sara observed a change in colour of NaoH solution by using 3 mL of H2SO4, how many mL of NaOH did she add to the test tube initially?
Ans: 3 mL of H2SO4 will be 60 drops, which will neutralise 6 mL of NaOH
| S.No. | Volume of dil NaOH taken (mL) | Drops of dil H2SO4 used |
| 1 | 2 | 20 (1 mL) |
| 2 | 3 | 30 (1.5 mL) |
| 3 | 4 | 40 (2 mL) |
| 4 | 6 | 3 mL = 60 drops |
OR
Sara takes 10 drops of dilute H2SO4 in the test tube and adds two drops of phenolphthalein solution to it. Then she adds NaOH dropwise. Sara observes a change in colour after adding 20 drops of NaOH. What change in colour would she observe and why?
Ans: Colour will change from colourless to pink. Phenolphthalein in colourless in acids and turns pink in basic solution.
C. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the above experiment. Which of the following is true and why? The reaction is a:
(a) neutralisation and double displacement reaction
(b) neutralisation and precipitation reaction
(c) precipitation and double displacement reaction
(d) neutralisation, double displacement as well as precipitation reaction.
Ans: 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(a) neutralisation and double displacement reaction.
Base NaOH is getting neutralised and forming salt + water. It is double displacement as Na+ ions are being replaced by H+ and OH– by SO42-. It is not precipitation reaction because Na2SO4 is soluble in water.
29. Attempt either option A or B.
A. A hydrocarbon with the formula CxHy undergoes complete combustion as shown in the following equation: (5)2CxHy + 9O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
(a) What are the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’?
Ans: x = 3, y = 6
(b) Give the chemical (IUPAC) name of the hydrocarbon.
Ans: Propene
(c) Draw its electron dot structure.
Ans: 
(d) Name the alcohol which on heating with conc. H2SO4 will produce the above hydrocarbon CxHy.
Ans: Propanol
(e) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of CxHy with hydrogen gas in presence of Nickel.
Ans: C3H6 + H2 →Ni→ C3H8
CH2=CH-CH3 + H2 →Ni→ CH3-CH2-CH3
OR
The electronic structures of atoms P and Q are shown below:
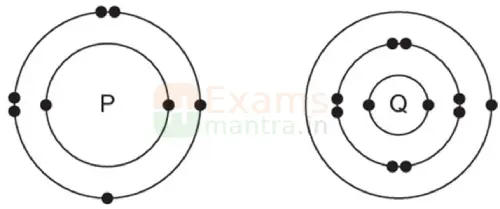
Based on the information given above, answer the following questions:
(a) If P and Q combine to form a compound, what type of bond is formed between them?
Ans: Ionic bond
(b) Give the chemical formula of the compound formed.
Ans: Q2P
(c) The compound so formed is dissolved in water. Is the resultant solution acidic or basic in nature? Justify your answer.
Ans: Basic, metallic oxides are basic in nature.
(d) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between ‘Q’ and ethanol.
Ans: 2C2H5OH +2Q → 2C2H5OQ + H2
(e) What will be the formula of the compound formed when ‘P’ undergoes bonding with carbon?
Ans: CP2
SECTION – C (PHYSICS – 25 Marks)
30. Arnav was making notes and he wrote down the following statements from his understanding of reflection from curved surfaces. (1)
I. Concave mirrors can produce both real and virtual images depending on the position of the object.
II. Convex mirrors always produce real, inverted images regardless of the object’s position.
III. In both concave and convex mirrors, the image location can be determined using the mirror formula 1/𝑓=1/𝑣+1/𝑢 where f is the focal length, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance.
Choose from the following the correct option that lists the correct statements about reflection from curved surfaces.
A. I and II
B. I, II and III
C. II and III
D. I and III
31. Choose the correct option from the below which explains the reason for us to perceive the day sky as blue. (1)
A. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, shorter wavelengths, such as blue are scattered more than other colors
B. The sky appears blue because all colors are scattered equally, but blue light is stronger and more visible to the human eye
C. The blue color of the sky is due to longer wavelengths like red and orange scattering more than shorter wavelengths, making blue stand out more
D. The atmosphere contains blue-colored particles that give the sky its blue appearance
32. Assertion (A): A point object is placed at a distance of 26 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 26 cm. The image will not form at infinity. Reason (R): For above given system the equation 1/𝑓=1/𝑣+1/𝑢 gives v = ∞. (1)
A. Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
B. Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A
C. A is true but R is false
D. A is false but R is true
33. The below image shows the formation of an image with an optical instrument. (2)
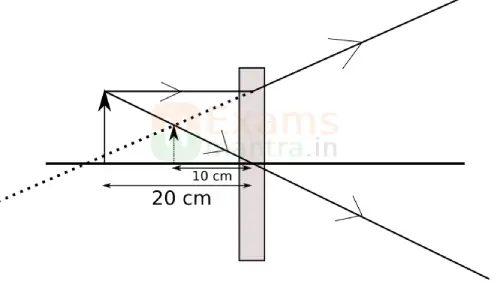
A. Identify the optical instrument (shown schematically as a rectangle) in the image.
Ans: The optical instrument shown in the figure is a concave lens.
B. What type of image is formed in this case?
Ans: The image formed is a virtual image.
C. Based on the measurements given in the image, calculate the focal length of the instrument.
Ans: To find the focal length for of a concave lens, we can use the lens formula: 1/𝑓 = i/𝑣-1/𝑢
where:
𝑢 = – 20 cm (object distance, taken as negative for concave lenses),
𝑣 = – 10 cm (image distance, also taken as negative since the image formed by a concave lens is virtual).
Solution: Substitute the values into the lens formula: 1/𝑓 = (i/-10) – (1/-20)
Simplify the terms: 1/𝑓 = (i/-10) – (1/-20)
Find a common denominator: 1/𝑓 = -(2/20) + (1/20) = -(1/20)
Solve for 𝑓: 𝑓 = -20 cm
34. Attempt either option A or B. (2)
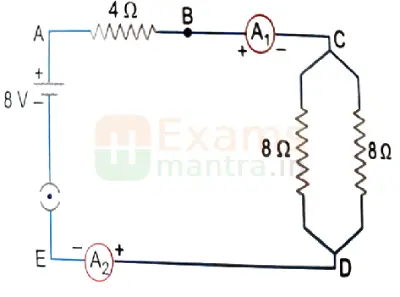
A. Find out the following in the electric circuit given in the figure:
(i) Effective resistance of two 8 ohm resistors in the combination.
Ans: R = R1R2 / R1+R2 = 8×8 / 8+8 = 4 ohms
(ii) Current flowing through the 4-ohm resistor
Ans: I = V/R = 8 / (4+4) = 1 A
OR
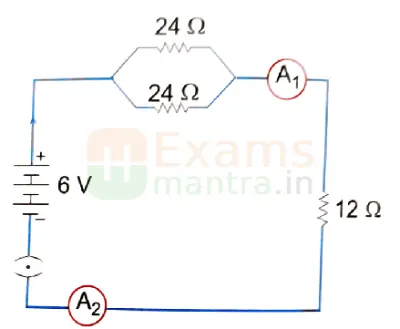
B. Study the circuit and find out:
(i) Current in 12 ohm resistor
Ans: 1/Rp = 1/R1 + 1/R2 = 1/24 + 1/24 = 2/24
Rp = 12 ohms
RT = Rp + 12 = 24 ohms
I = V/R = 6/24 = 0.25 A
(ii) Difference in the readings of ammeter A1 and A2 if any
Ans: Same readings of A1 and A2
35. The below image shows a corrective measure for a particular defect of vision. (3)
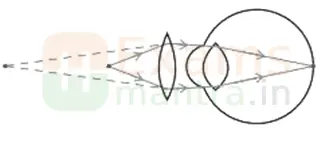
(i) Identify the defect of vision and state what kind of lens is used to correct this deficiency.
Ans: Hypermetropia is the deficiency in vision and the lens is convex lens.
(ii) Draw and label a ray diagram that shows the defect of vision in the above case before correction.
Ans:
36. A student needs to make a 0.12 Ω resistor. She has some copper wire of 0.80 mm diameter. Resistivity of copper is 1.8 × 10–8 Ωm (3)
(i) Determine the cross-sectional area of the wire.

(ii) Calculate the length of wire required for the 0.12 Ω resistor

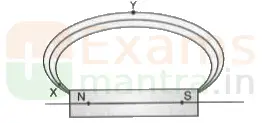
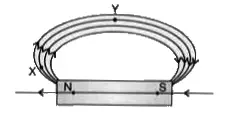
37. Magnetic field lines are shown in the given diagram. A student makes a statement that the magnetic field at X is stronger than at Y. (3)
(i) Explain with reason if the student’s claim is correct.
Ans: Closeness of magnetic field lines is directly related to strength of magnetic field.
Strength of magnetic field at point X (pole) is more than point Y.
If the student redraws the diagram he/she should mark arrows correctly from North to South.
(ii) Also redraw the diagram and mark the direction of magnetic field lines.
38. The below image is that of a Digital Single Lense Reflector (DSLR) Camera which are used to take high resolution photographs by professional photographers. The second image of the above two is a schematic diagram of how an image is formed on the sensor of the camera. Based on your understanding of the lenses, answer the following questions. (4)
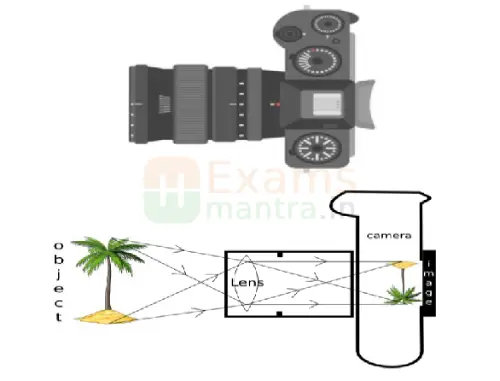
A. What type of lens is used in the DSLR camera shown in the image?
Ans: Convex Lens
B. What type of image is formed on the sensor?
Ans: Real and Inverted
Attempt either subpart C or D.
C. A photographer is using a DSLR camera with a lens of focal length f=50 mm to take a close-up photograph of a small object. The lens projects an image onto the camera sensor that is located 60 mm behind the lens. Calculate the object distance (i.e., the distance between the object and the lens).

OR
D. A photographer is using a DSLR camera to take a picture of a flower. The flower is positioned 150 mm away from the camera lens. The actual height of the flower is 80 mm, and the image height formed on the camera’s sensor is measured to be 20 mm. Calculate the focal length of the camera lens.

39. Attempt either option A or B. (5)
A. The arrangement of resistors shown in the above figure is connected to a battery.;
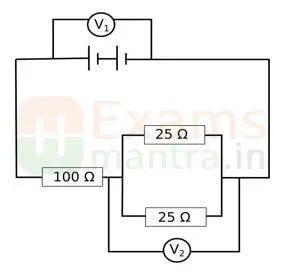
The power dissipation in the 100 Ω resistor is 81 W. Calculate
(i) the current in the circuit
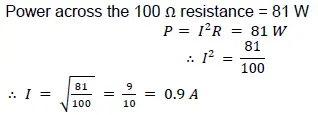
(ii) the reading in the voltmeter V2
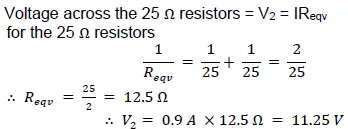
(iii) the reading in the voltmeter V1
Ans: Voltage across 100 Ω = 𝑉100 = 𝐼𝑅 = 0.9 𝐴 ×100 Ω = 90 𝑉
∴ 𝑉1 = 90 𝑉 + 11.25 𝑉 = 101.25 𝑉
B. An electric heater consists of three similar heating elements A, B and C, connected as shown in the figure above. Each heating element is rated as 1.2 kW, 240 V and has constant resistance. S1, S2 and S3 are respective switches.
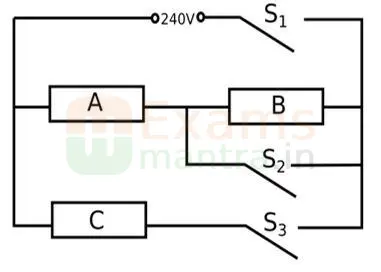
The circuit is connected to a 240 V supply.
(i) Calculate the resistance of one heating element.
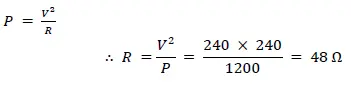
(ii) Calculate the current in each resistor when only S1 and S3 are closed.

(iii) Calculate the power dissipated across A when S1, S2 and S3 are closed.
Ans: Power across A for S1, S2, S3 closed
𝑃𝐴 = 𝐼2𝑅 = 52×48 = 1200 𝑊 = 1.2 𝐾𝑊
Other Related CBSE Class 10 Sample Question Papers with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 English Comm 101 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 English Comm 101 Sample Question Paper 2026 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 English LL 184 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 English LL 184 Sample Question Paper 2026 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi A 002 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi B 085 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 IT Code 402 Pre Board Sample Question Paper 2024 – with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 IT Code 402 Pre Board Sample Question Paper 2025 – Set 1 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 IT Code 402 Pre Board Sample Question Paper 2025 – Set 2 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 IT Code 402 Sample Question Paper 2024 – SET 1 – with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 IT Code 402 Sample Question Paper 2024 – SET 2 – with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 IT Code 402 Sample Question Paper 2024 – SET 3 – with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Standard 041 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sample Question Paper 2023 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sample Question Paper 2024 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sample Question Paper 2026 with Solution
- Class 10 AI Code 417 Sample Question Paper 2024 with Solution
- Class 10 AI Code 417 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- Class 10 CA Code 165 Sample Question Paper 2025
- Class 10 CA Code 165 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- Class 10 CA Code 165 Sample Question Paper 2026 with Solution
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Sample Question Paper 2022 with Solution – Term 2
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Sample Question Paper 2023 with Solution
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Sample Question Paper 2025 with Solution
- Class 10 Science Code 086 Sample Question Paper 2025
- Class 10 Science Code 086 Sample Question Paper 2026 with Solution
